GPS tracking offers immense benefits to enterprises, facilitating the seamless monitoring of vehicles and personnel. However, this technology’s widespread adoption raises privacy concerns among those who prefer not to share their location. Inexpensive yet powerful tracking devices now make it easier to trace movements, highlighting both the conveniences and controversies of this advancing trend. Ultimately, gps tracking reflects our society’s evolving relationship with technology and the complexities of balancing progress with individual freedoms.
- What Exactly Is a GPS Jammer?
- How does a GPS jammer operate?
- Is it Legal to Use GPS Jammers?
- Who Uses GPS Jammers?
- GPS Jammers and the Transportation Industry: Is There a Connection?
- How Can GPS Help With Jamming Detection?
What Exactly Is a GPS Jammer?
A GPS jammer is a small, self-contained transmitting device designed to interfere with GPS devices by sending radio signals on the same frequency. This interference prevents the GPS device from accurately determining its location. While commonly referred to as a ‘GPS jammer,’ it’s important to note that the term ‘GPS’ should encompass other global navigation systems like BeiDou. These jammers are typically used temporarily due to their low power consumption and quick startup times. Despite being illegal, various types of cheap gps jammers can be easily purchased online, including physical shields and specialized jammers for Wi-Fi/Bluetooth, remote controls, spy cameras, and drones.
How does a GPS jammer operate?
The user plugs the gps jammer into the car’s auxiliary power outlet, or for handheld variants, powers it up with the included battery. Positioned close to the mounted GPS tracker, this device, when switched on, emits a disruptive signal. This jamming signal, spanning a 5 to 10-meter radius, effectively disrupts the reception of GPS satellite signals, typically targeting non-military frequencies. To grasp the jammer’s mechanism, it’s essential to understand the Global Positioning System’s (GPS) inner workings. GPS trackers receive microwave signals broadcasted by a network of satellites orbiting Earth. By capturing signals from at least four satellites, the tracker pinpoints its location through complex time calculations and trilateration techniques. The jammer exploits this dependency, disrupting these vital satellite signals to obscure the receiver’s global position.
GPS tracking devices transmit position and speed data to a monitoring location via cellular networks. However, various factors can disrupt this transmission. In the early days of the Beidou satellite network, position measurement relied on two satellites and ground base stations. Nowadays, satellite failures or solar flares can temporarily interrupt GPS signals. But a more significant threat is GPS jammers. These devices emit radio signals or noise at the same frequency as GPS, covering or distorting satellite signals. When this occurs, the GPS device becomes unable to calculate its location due to the interference masking the satellite signals. It’s crucial to be aware of these disruptions and take necessary precautions to ensure reliable GPS tracking.
Is it Legal to Use GPS Jammers?
Using GPS jammers is illegal in many nations, including the U.S., Canada, and the UK, and carries harsh penalties. In the U.S., the 1934 Communications Act bans the sale, marketing, or use of these devices, while Canada’s Radiocommunication Act prohibits their import, manufacture, distribution, sale, possession, and use. Violators in the U.S. face fines up to $100,000 or more, imprisonment, and loss of equipment.
Who Uses GPS Jammers?
The reasons for using GPS jammers vary widely. Originally devised for military purposes, these devices were created by the government to serve a specific need in operations. Concealing vehicle location is crucial in certain military missions, where it can enhance success and safety. The technology acts as a protective cloak, providing privacy and an overall advantage in high-risk scenarios. However, its use is not limited to the military. Some speeding drivers may employ GPS jammers to evade police detection and fines. Criminals have also been known to use them, possibly to conceal vehicle theft or avoid tolls and mileage charges. In the realm of business, a driver within a fleet might utilize a GPS jammer to prevent their employer from monitoring their movements in company vehicles. The possibilities are diverse, but it’s important to note that the legal use of GPS jamming equipment is highly restricted.
GPS Jammers and the Transportation Industry: Is There a Connection?
GPS jammers pose a significant nuisance and concern for both law enforcement and the transportation industry. These devices illegally interfere with GPS asset tracking, also known as fleet tracking or telematics, disrupting a crucial source of business intelligence for many companies. Fleets rely on telematics to monitor and manage various aspects of their operations, including fuel consumption, idling time, driving behavior, and engine health. However, some drivers use jamming devices to conceal their location from transportation companies, leading to increased risks and unnecessary costs. The use of GPS jammers not only violates regulations but also poses potential dangers, making it a serious issue that needs to be addressed.
How Can GPS Help With Jamming Detection?
Choosing the best signal detection device is key to ensuring your safety and privacy. These devices can help you locate jammers, signal transmitters, tracking devices, and even anti-tracking devices. Moreover, some advanced devices can promptly notify transportation companies of potential threats based on real-time signal analysis, significantly reducing unwanted interruptions. Investing in a high-quality signal detection device is an investment in your peace of mind and security.
GPS jammers are illegal devices that can interfere with GPS signals, causing navigation and other equipment to malfunctioin. Using a GPS jammer may pose safety hazards and may be subject to legal sanctions. Therefore, I cannot provide information on how to make or use GPS jammers.
If you have any questions about GPS technology or other related topics, please feel free to ask me and I will do my best to answer them.
DIY a GPS jammer in simple steps. Learn about the materials needed, circuit design, and assembly process. Follow this guide to create your own effective GPS signal blocker.
- Step 1: Required Components and Materials
- Step 2: Build the Circuit
- Step 3: Integrate the VU Meter
- Step 4: Test Your GPS Jammer
Step 1 Required Components and Materials
For this project, you’ll need various components, each with a specific purpose. Detailed below is an itemized list, briefly explaining the role of every piece. Assemble them all to make your project a success.
| How to Make a GPS Jammer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To create a GPS jammer, you will need the following components and understand their functions: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 2 Build the Circuit
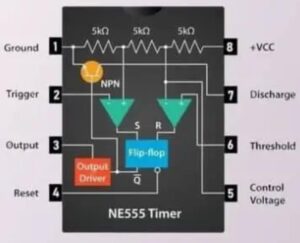
Ready to disrupt GPS frequencies? Our project guides you through building a circuit on a breadboard – no soldering needed! Start by placing the NE555 timer IC, resistors, capacitors, and an LED onto the breadboard, following our schematic diagram. Use jumper wires to connect them, then power up with a 9-volt battery. Once the red LED lights up, you’ll know your circuit is generating the radio frequency signal to jam GPS frequencies. Easy, right? Get started now!
Step 3 Integrate the VU Meter
To monitor and optimize the performance of your GPS jammer, install a Volume Unit (VU) meter to measure the strength of its generated radio frequency signal. Here’s how to proceed: Connect the VU meter’s input terminals directly to the output of your jammer circuit for accurate signal strength readings. Ensure tight connections to avoid any discrepancies in measurement. Power up your circuit after integration. The VU meter’s needle or LED indicators will respond, displaying the signal strength in decibels (dB). Interpret these readings carefully. A higher dB value signifies a stronger signal. If needed, calibrate your VU meter for precise measurements. This step enhances the accuracy of your readings, further optimizing the performance of your GPS jammer.
Step 4 Test Your GPS Jammer
Testing your jammer is the culmination of your project, ensuring its effectiveness in disrupting GPS signals. Before commencing, confirm that your testing environment is secure and clear of any delicate electronics to prevent any undesired interference. To initiate the test, activate your jammer and observe any provided indicators, such as a red LED, for insights into its operational status. Utilize a GPS receiver module or a device equipped with GPS capabilities for the testing process. Begin by verifying a strong signal on your GPS device before introducing the jammer. As you gradually bring the jammer closer, monitor the GPS device for any changes. Signs of the jammer’s effectiveness include signal disruptions or loss, evident through slower update times on the GPS module or a “searching for signal” status. Additionally, you may notice a decrease in the number of satellites detected by the GPS module, further confirming the jammer’s functionality.
