- What is a Mobile Jammer?
- How Does a Mobile Jammer Work?
- Detailed Block Diagram Analysis
- Mobile Jammer Circuit Diagram Explained
- Types of Mobile Jammers
- Applications of Mobile Jammers
- Frequently Asked Questions
Mobile jammers are fascinating devices that disrupt cellular communication by transmitting signals on the same frequency as mobile phones. Originally developed for military use, these devices have found applications in civilian settings like classrooms, hospitals, and government facilities. This comprehensive guide explores the working principles, components, types, and legal implications of mobile jammers, providing valuable insights into this controversial technology.
What is a Mobile Jammer?
A mobile jammer is an electronic device designed to block cellular communication by transmitting radio signals on the same frequencies used by mobile phones. When activated, it creates interference that prevents phones within its range from connecting to cell towers. The first jamming devices were military tools used to disrupt enemy communications. Today, they serve various purposes from maintaining silence in libraries to security applications in prisons.
How Does a Mobile Jammer Work?
The fundamental principle behind mobile jammers involves transmitting powerful radio signals that overpower the communication between cell phones and towers. This creates a “denial of service” attack at the radio frequency level. The jammer must broadcast across all frequencies used in the target area (typically 450MHz, 800MHz, 900MHz, 1800MHz, and 1900MHz bands) to effectively block all cellular traffic.
Key Components of a Mobile Jammer
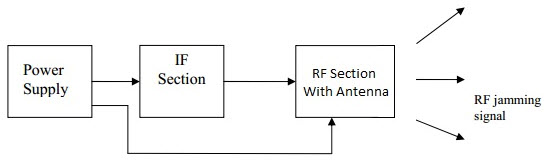
The mobile jammer consists of three main sections that work together to disrupt cellular signals:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Power Supply | Provides electrical power to all components |
| IF Section | Generates interference signals and noise |
| RF Section | Amplifies and transmits the jamming signal |
Detailed Block Diagram Analysis
The complete mobile jammer system can be understood through its block diagram components:
Power Supply Section
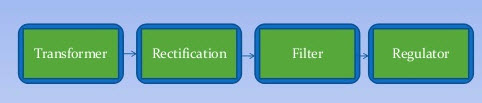
The power supply converts standard AC voltage to the DC voltages required by the jammer’s components. It includes:
- Transformer: Steps voltage up or down as needed
- Rectifier: Converts AC to DC (full-wave or half-wave)
- Filter: Smoothes the DC output using large capacitors
- Regulator: Maintains constant voltage levels
IF (Intermediate Frequency) Section
The IF section generates the interference patterns that disrupt cellular signals. It contains:
- Noise generator: Creates random electronic signals
- Mixer: Combines different frequency components
- Triangular wave generator: Produces sweeping interference
RF (Radio Frequency) Section
This is the core of the jammer that actually transmits the disruptive signals. Key elements include:
- Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO): Generates the RF signal
- Power Amplifier: Boosts signal strength
- Antenna: Radiates the jamming signal
Mobile Jammer Circuit Diagram Explained
The complete circuit combines three essential sub-circuits that work together to create the jamming effect:
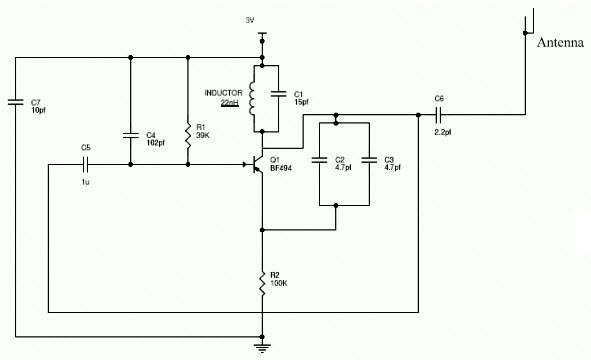
- RF Amplifier: Uses transistor Q1 with capacitors C4, C5 and a resistor to amplify the signal
- Tuning Circuit: Consists of capacitor C1 and inductor L1 forming an oscillator
- Voltage Controlled Oscillator: Adjusts frequency based on input voltage
Types of Mobile Jammers
Different environments require specialized jamming solutions:
- Remote Controlled Jammers: Operated from a distance for security applications
- Adjustable Jammers: Allow frequency and power adjustment
- School & Prison Jammers: Designed for institutional use with controlled range
- Explosion Proof Jammers: For use in hazardous environments
- Police & Military Jammers: High-power devices for tactical operations
- Portable Jammers: Compact, battery-powered units
Applications of Mobile Jammers
While controversial, jammers serve legitimate purposes in specific contexts:
- Maintaining silence in libraries and classrooms
- Preventing disturbances in meeting rooms and theaters
- Enhancing security in prisons and military installations
- Protecting sensitive areas from remote detonations
- Preventing cheating in examination halls
- Maintaining decorum in religious institutions
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a mobile jammer disrupt phone signals?
A mobile jammer works by transmitting powerful radio signals on the same frequencies used by cell phones. This creates interference that overwhelms the normal communication between phones and cell towers, effectively creating a “denial of service” at the radio level.
Is it legal to use mobile jammers?
In most countries, mobile jammers are illegal for civilian use. They are typically restricted to military, law enforcement, and certain government applications. Unauthorized use can result in significant fines and legal consequences.
What’s the effective range of a mobile jammer?
The range varies by model, from a few meters for portable devices to several hundred meters for high-power units. Factors like transmitter power, antenna design, and environmental conditions all affect the effective jamming range.
Can jammers block all types of mobile networks?
Advanced jammers can block multiple network types (GSM, CDMA, 3G, 4G/LTE) simultaneously by targeting all relevant frequency bands. However, simpler models may only affect specific network types.
Why were mobile jammers originally developed?
The military developed early jammers to disrupt enemy communications during conflicts. These devices allowed forces to block radio communications while maintaining their own secured channels.
Do jammers affect other wireless devices?
Depending on their design, some jammers may interfere with other wireless services operating on similar frequencies, including WiFi networks, Bluetooth devices, and emergency communications if not properly configured.