- What Is RF Anti-Jamming Technology?
- How Does Anti-Jamming Counteract Signal Interference?
- Why Are Anti-Jamming Devices Ineffective Against GPS Jammers?
- Practical Steps to Neutralize Anti-Jamming Systems
- Common Misconceptions About Anti-Jamming Technology
- FAQ: RF Anti-Jamming Technology
RF anti-jamming technology is designed to counteract signal interference, but its effectiveness depends on the type of jammer used. This article explores how anti-jamming devices work, their limitations, and practical steps to bypass them. We’ll analyze methods like antenna nulling, frequency hopping, and why gps jammers like the B39EVO render anti-jamming systems ineffective. Whether you’re a security professional or a tech enthusiast, this guide provides actionable insights into signal protection and disruption.
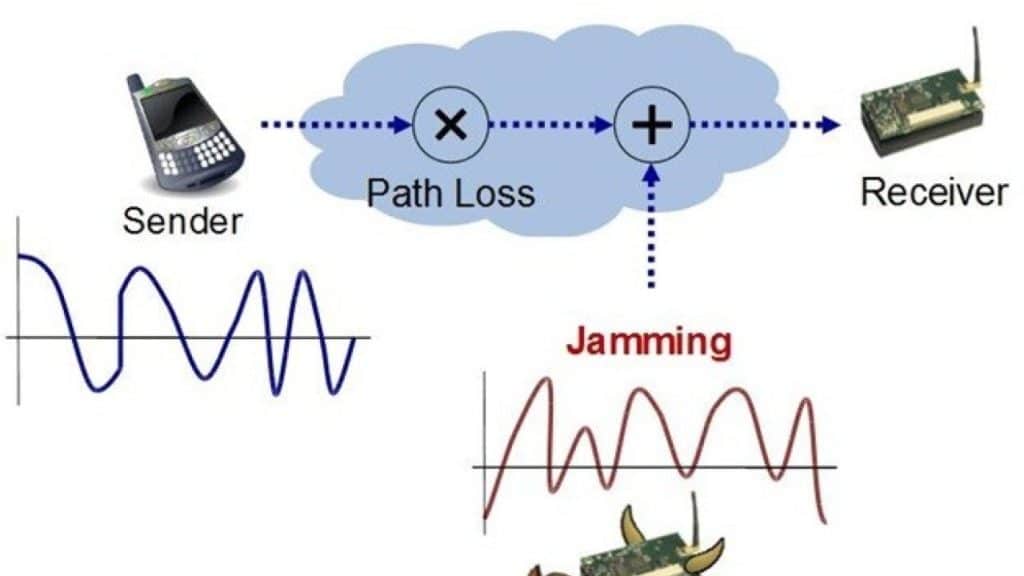
What Is RF Anti-Jamming Technology?
Anti-jamming technology detects and mitigates interference in GSM frequencies within a defined area. It works by identifying overpowering signals from jammers—devices that disrupt communication by transmitting noise at the same frequency as the target signal. However, these countermeasures are only effective against low-quality cellular jammers, not advanced GPS jammers.
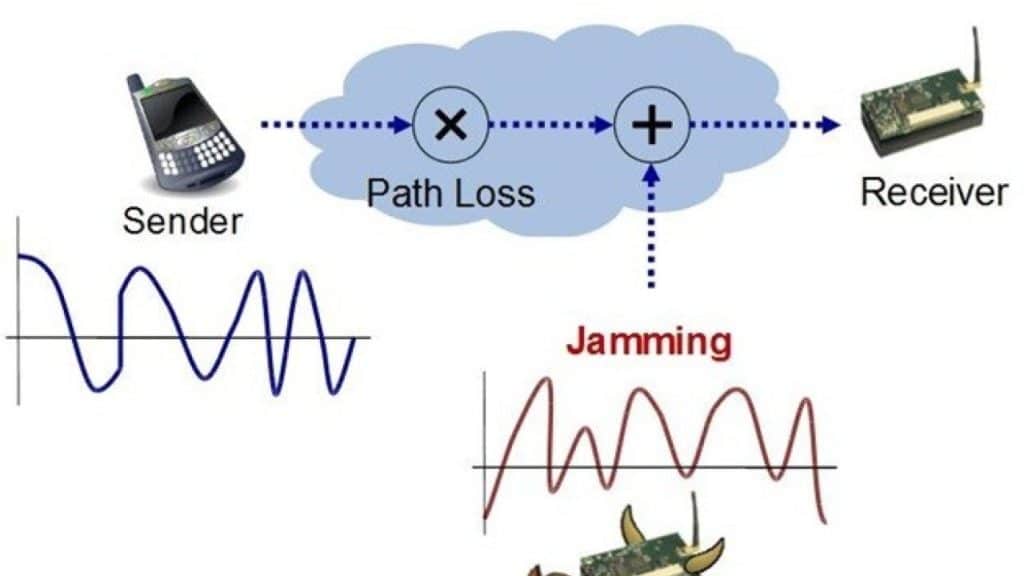
How Does Anti-Jamming Counteract Signal Interference?
One advanced method involves steering antennas (mechanically or electronically) to create a “null” zone toward the jammer. This reduces the jammer’s signal strength while minimally affecting legitimate communications. Other techniques include frequency hopping (switching channels rapidly) and encryption to prevent signal hijacking.
Why Are Anti-Jamming Devices Ineffective Against GPS Jammers?
GPS jammers like the B39EVO operate on different frequencies than cellular jammers. Anti-jamming systems designed for GSM bands cannot detect or block GPS interference. For example, activating a Raptor or PRO10 jammer on GPS frequencies first, followed by cellular bands, renders anti-jamming alarms useless within 60 seconds.
Practical Steps to Neutralize Anti-Jamming Systems
- Power on the jammer (e.g., Raptor/PRO10) with GPS frequencies enabled.
- After 30 seconds, activate remaining cellular frequency switches.
- Within another 30 seconds, the anti-jamming device becomes ineffective.
Some systems may transmit alarms via GPS frequencies, but dedicated radio frequency jammers can block these signals.
Common Misconceptions About Anti-Jamming Technology
Many assume anti-jamming devices offer universal protection, but their efficacy is limited to specific frequency ranges. Understanding these limitations helps users explore alternatives, such as multi-frequency jammers or physical signal shielding.
FAQ: RF Anti-Jamming Technology
How does an anti-jammer detect interference?
It scans for abnormal signal power levels in GSM bands and triggers countermeasures like frequency hopping.
Can anti-jamming block all types of jammers?
No—only low-power cellular jammers. GPS and military-grade jammers often bypass these systems.
What’s the difference between jamming and spoofing?
Jamming overpowers signals with noise; spoofing mimics legitimate signals to deceive receivers.