Crafting a DIY GPS jammer? Here’s an SEO-optimized step-by-step guide! Learn how to build a gps jammer from scratch, starting with selecting essential components and materials. We’ll guide you through building the circuit, integrating a VU meter, and finally, testing your GPS jammer. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or a DIYer, this comprehensive guide will ensure your success in creating a reliable GPS jammer. Explore the steps now!
- What is a Signal Jammer? Required Components & Materials
- Build the Circuit – Step-by-Step Guide
- Adding a VU Meter: Optimize Your Audio Monitoring
- Test Signal Jammer
- GPS Jammer: Responsible Usage Guide
What is a Signal Jammer? Required Components & Materials
| Component | Function |
| NE555 Timer IC | Integral part for creating precision waveforms and time delays, essential for accurate signal manipulation. |
| 47 pF Ceramic Capacitor | Vital for storing and releasing electrical energy, stabilizing voltage and ensuring smooth circuit operation. |
| 0.01 µF Ceramic Capacitor | Another crucial capacitor for voltage stabilization, providing the necessary support for consistent circuit performance. |
| 10 K Resistor | Fundamental for limiting electrical current flow and setting specific currents, ensuring circuit safety and efficiency. |
| 220 Ω Resistor | Another vital resistor for current limitation and setting, ensuring the stability and reliability of the circuit. |
| 100 µF Electrolytic Capacitor | High-capacity capacitor that smooths out voltage fluctuations, ensuring stable and consistent operation of the assembled circuit. |
| Red LED | Used as a visual indicator for signals or power status, providing instant feedback on the circuit’s operational status. |
| 9-Volt Battery | Reliable power source for the assembled components, ensuring uninterrupted operation and long-lasting performance. |
| Breadboard | An indispensable tool for prototyping and testing circuit designs, allowing for easy assembly and modification without soldering. |
| GPS Receiver Module and Antenna | Components used for testing the real-world application and effectiveness of the assembled circuit, crucial for optimizing performance. |
Build the Circuit – Step-by-Step Guide
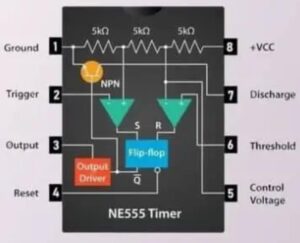
To construct a highly effective GPS jammer, the breadboard serves as your fundamental workspace. Designed to facilitate testing without the need for soldering, it enables seamless circuit prototyping. Prior to initiating the build, thoroughly review the GPS jammer’s schematic diagram to ensure a precise component placement. Commence by securely positioning the NE555 timer IC on the breadboard, adhering strictly to the schematic’s layout. Subsequently, place each resistor, capacitor, and LED in their designated spots, aligning precisely with the diagram’s guidelines.
Utilize jumper wires to meticulously establish the crucial connections between these components, ensuring electrical conductivity and stability. Once the circuit is assembled, power it with a reliable 9-volt battery. If the red LED illuminates, it signifies a successful build, indicating that the circuit is functioning optimally and emitting the desired radio frequency signal capable of disrupting GPS frequencies. This crucial step ensures the jammer’s efficacy and paves the way for further advancements in GPS jamming technology.
Adding a VU Meter: Optimize Your Audio Monitoring
Start by positioning the VU meter’s input terminals directly in line with the output of your jammer circuit. This ensures that the meter captures the exact signal strength being emitted. Secure the connections to prevent any inaccuracies in readings.
Once integrated, power on your jammer circuit and observe the VU meter’s needle or LED indicators. These will display the signal’s strength in decibels (dB), giving you a clear indication of the signal’s potency. A higher dB value signifies a stronger signal, allowing you to fine-tune your jammer for maximum effectiveness.
To ensure precise readings, some VU meters offer calibration options. This feature optimizes the performance of your GPS jammer, providing you with accurate signal strength measurements. Take advantage of this functionality to get the most out of your jamming device.
Test Signal Jammer
First, activate the jammer and keep a close eye on any indicators, such as a red LED, for instant feedback on its operational status. For testing purposes, utilize a GPS receiver module or device with GPS functionality. Ensure the device has a clear signal before introducing the jammer.
As you gradually bring the jammer closer, monitor the GPS device closely. Signs of signal disruption or loss indicate that the jammer is functioning as intended. Look for telltale signs like slower update times on the GPS module or a “searching for signal” status. You may also notice a notable drop in the number of satellites detected by the GPS module.
GPS Jammer: Responsible Usage Guide
Crafting a GPS jammer may seem like an enticing DIY challenge, but it’s crucial to uphold legal and ethical boundaries. In numerous countries, including the United States, gps jammers are outlawed due to their potential for disrupting crucial communication networks and emergency services. Prioritize safety and responsible technology usage. Remember, while the allure of experimentation may be strong, ethical and legal considerations should always prevail. Use GPS jammer responsibly, ensuring your actions do not infringe upon the rights and safety of others.
