RSSI, which stands for Received Signal Strength Indicator, is a crucial metric for assessing Wi-Fi performance. In this article, you’ll learn all about RSSI, and we’ll provide you with a detailed guide on how to measure it using the Netspot Wi-Fi Signal Strength Meter.
What is RSSI and Why is it Important?
RSSI is a crucial metric that network engineers regularly depend on. Understanding what RSSI is will provide you with valuable insights into your WiFi network’s performance, empowering you to troubleshoot issues related to coverage and performance. This knowledge is vital to ensure you have the best possible experience when using your WiFi network
What Does RSSI Stand For?
The acronym RSSI stands for Received Signal Strength Indicator. Let’s explain what each part of this acronym means:
Received: Wireless signals are typically sent by a WiFi router and received by WiFi devices, such as smartphones, laptops, wireless security cameras, and others. The word received indicates that RSSI is concerned with wireless signals at the time when they’re received by WiFi-enabled devices.
Signal strength: RSSI measures the power present in a received radio signal. In other words, it measures WiFi signal strength.
Indicator: This is just another word for “measurement,” which is what RSSI is.
“What is the RSSI signal strength?
WiFi signals start gradually losing power from the moment they’re transmitted. Since RSSI is a measurement of received signal strength, it’s always negative, indicating how much signal strength has been lost.
In the real world, it’s impossible to achieve an RSSI of 0, but you want to get as close to 0 as possible. To tell you how close you are, Vendors and chipset makers typically break down RSSI values into several levels.
Each RSSI level represents a certain power level in milliwatts or decibels referenced to one milliwatt (dBm). When you test WiFi signal strength, you should always strive to discover your RSSI level. You can then use the information to determine how much room for improvement there is.
The Significance of RSSI: Why It Matters
Understanding the purpose of RSSI is crucial for WiFi users. Although internet speed tests are a convenient way to measure download and upload speeds, they do not convey the full picture due to several factors that can impact connection quality. Signal strength, as determined by RSSI measurements, is one such factor, making it imperative to be aware of it. As internet speed tests do not provide RSSI data, it is recommended to use reliable WiFi signal strength apps for Mac or Windows to keep track of the measurement.
Decoding the Significance of RSSI Levels
As we’ve already explained in the previous section of this article, RSSI values represent the relative quality of a received signal on a device.
RSSI indicates the power level being received after any possible loss at the antenna and cable level. The higher the RSSI value, the stronger the signal. When measured in negative numbers, the number that is closer to zero usually means better signal strength. As an example, -50 is a pretty good signal, -75 – is fairly reasonable, and -100 is no signal at all.
Here’s a quick overview of acceptable signal strength levels:
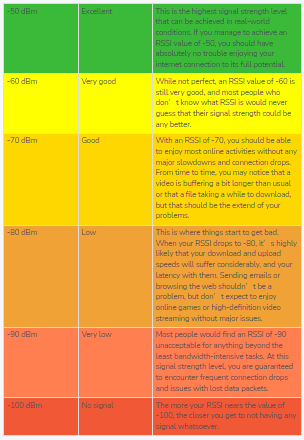
RSSI is expressed in arbitrary units, and there’s no standardized relationship of any particular physical parameter to the RSSI reading.
RSSI Values and dBm
Even though RSSI and dBm are different units of measurement they both indicate the signal strength.
What Does dBm Mean?
The dBm is a power ratio of the measured power as references to one mW (milliwatt). While dBm is an absolute index, the RSSI is a relative one. RSSI is often indicated using dBm even though the relationship between the two measurements is arbitrary, as evident from the dBm meaning explanation above.
Converting RSSI to dBM
The RSSI to dBM chart above can help you understand what different RSSI values mean. In practice, you shouldn’t worry too much about the mechanics of converting RSSI to dBM because there’s no RSSI-dBm standard that all vendors universally follow.
What you should worry about instead is how to increase WiFi signal strength to reach higher RSSI values and RSSI levels.
Improving RSSI Values and dBm
There’s a lot that you can do to improve your RSSI values and dBm:
Upgrade your router: Modern routers feature much more signal strength-e
nhancing technologies than their older counterparts, so purchasing a faster router is often the simplest (but not the cheapest) way to improve your RSSI values.
Get a stronger antenna: Some routers come with replaceable antennas. If your router is among them, then you can buy a stronger antenna for an instant signal strength boost.

To improve your WiFi signal strength, consider relocating your router to a more appropriate location based on the results of a proficient WiFi signal analyzer. On Windows 10, you can check the strength of your WiFi signal and create a visual map of its coverage, enabling you to identify areas with inadequate coverage and determine the best spot for your router. This strategy will help you reduce the loss of signal strength and enhance your Internet browsing experience.
Change router settings: Modern routers support two or three different bands, and each band is divided into multiple channels. You can change your router settings to prioritize less used bands and channels over those that are used by other routers in your area.
Eliminate sources of signal interference: Everything from large electronic appliances to cordless phones can be a source of signal interference. By eliminating as many sources of signal interference as possible, you can reliably improve your signal strength.
What is the relationship between RSSI and signal quality?
Even though there is no universal solution, we’ll try to break down the approximate interrelation between RSSI and quality percentage.
Signal Quality is a value from 0% to 100%. The higher the number the better the link quality. These are theoretical numbers for ideal conditions in regards to local noise. Depending on the system and device you use it can be determined differently and is based on signal strength and SNR margin. Usually the signal is usable if the quality is above the level of 25-30%.

SNR margin = signal(dBm) – noise(dBm)
E.g. if signal (RSSI) = -55db, and noise = -85db, then:
(-55db signal) – (-85db noise) = 30 SNR margin
Higher SNR margin values mean clearer signals. As an example, using the full 54 Mbps data rate will require at least 25 dB of SNR margin.
Generally,
db >= -50 db = 100% quality
db <= -100 db = 0% quality
For RSSI signal between -50db and -100db,
quality ~= 2 * (db + 100)
RSSI ~= (quality / 2) – 100
For example:
High quality: 90% ~= -55db
Medium quality: 50% ~= -75db
Low quality: 30% ~= -85db
Unusable quality: 8% ~= -96db
RSSI in 802.11 implementations
RSSI can help determine when the level of radio energy in the channel is lower than a certain point so that the network card is clear to send (CTS). At that time the packet of data can be sent.
The network monitoring tool like NetSpot allows an end user to observe an RSSI value while measuring the signal strength of a WiFi network. Just for reference, Cisco Systems cards have an RSSI_Max value of 100 and will report back 101 power levels.
The 802.11 standard does not give any definition of how RSSI value and power level in mW or dBm relate. Chipset makers and vendors give their own accuracy, granularity, and range for the actual power (mW or dBm). Also the range of RSSI values is individual, ranging from 0 to RSSI_Max. RSSI value is obtained during the preamble stage of getting an 802.11 frame, not from the full frame.
To understand and use your signal strength measurements for the most efficient channel planning decisions, NetSpot shows signal strength in two ways.
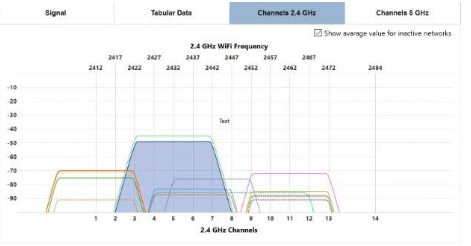
The Networks Chart visualizes the location of selected networks on the 2.4 or 5 GHz bands in relation to other networks, and displays the signal strengths for each of them.
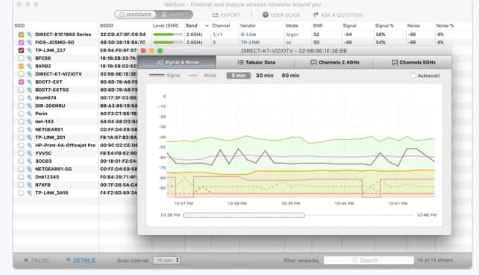
The Signal Strength graph visualizes the changes in your network’s signal strengths as you move around the space.
Experiencing problems despite acceptable signal strength?
If a WiFi scan app like NetSpot shows an acceptable signal strength but the connection remains problematic, it may be due to interference. Your computer’s WiFi adapter and NetSpot can identify sources of WiFi interference and help improve signal strength.
How to track signal strength with NetSpot:
Download and install NetSpot.
Launch the application and give it a few seconds to gather information about nearby WiFi networks.
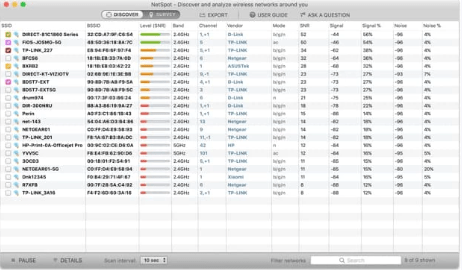
Double-click on the network you want to track to see signal strength displayed as a real-time chart.
SO, WE RECOMMEND
NetSpot
WiFi analyzer app runs on a MacBook (macOS 10.10+) or any laptop (Windows 7/8/10/11) with a standard 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax wireless network adapter.
| 4.8 969 User reviews |
#1 WiFi analyze app |
|
| 500K Users |
6 Years |
Cross-platform Mac/Windows |
What is RSSI?
The acronym RSSI stands for received signal strength indicator, which reflects the strength of a signal received by a device. This measurement gauges signal power after accounting for potential losses at the antenna and cable levels. A higher RSSI value indicates a stronger signal.
How does RSSI relate to signal quality?
Signal Quality goes from 0% to 100% — the higher the better, with 100% of course being a value that is theoretical given the ideal conditions. Signal quality can be determined differently based on the devices you are using as well as signal strength and SNR margin. Usually the signal is fine if the quality is above the level of 25-30%.
This is how RSSI is related to quality percentage (these are approximate values).
High quality: 90% ~= -55db
Medium: 50% ~= -75db
Low: 30% ~= -85db
Unusable: 8% ~= -96db
How to Interpret and Utilize Measurements of Signal Strength: A Guide
The relation between RSSI value and power level in mW or dBm is not universally defined in the 802.11 standard and varies among device makers, with RSSI values ranging from 0 to RSSI_Max. NetSpot offers two ways to facilitate the interpretation and utilization of signal strength measurements. Firstly, the Networks Chart displays the location and signal strengths of selected networks on the 2.4 or 5 GHz bands relative to other networks. Secondly, the Signal Strength graph presents the changes in signal strength values of your network as you move around.
What to Do When WiFi Issues Persist Despite Acceptable Signal Strength
If you have utilized a WiFi scanning application, such as NetSpot, and confirmed that signal strength levels are satisfactory, but you are still experiencing connectivity issues, the root cause could be interference. To address this, utilize NetSpot and your computer’s WiFi adapter to identify potential sources of interference and make changes to avoid it.
What is a good RSSI?
That depends on what you do online and your expectations. For most people who use the internet to browse the web, watch online videos, send emails, and play multiplayer video games, an RSSI of -70 is perfectly acceptable. But if you’re paying for a very fast internet connection and want to use it to its full potential, you want to get as close to -50 as you can.
Is RSSI 48 good?
RSSI is typically represented in a negative form, so the closer the value is to 0, the strong the received signal is. However, since RSSI is a completely arbitrary value that has no relationship to any particular physical parameter, it can also be represented in a positive form, where the RSSI value is 0 to 100, with 100 being the strongest signal possible. In that case, an RSSI of 48 is a fairly reasonable value that’s more than sufficient for most regular activities.
Is RSSI 55 good?
Yes, an RSSI value of 55 is generally considered to be good enough for most users and online activities. If measured in negative numbers (with 0 meaning the best signal possible and -100 the worst), then the relative quality of a received signal on a device is slightly worse, but still acceptable.
What is a good RSSI level for the Ring doorbell?
The Ring doorbell requires a fairly strong signal because it transmits high-quality video in real-time. The manufacturer recommends an RSSI between -65 and -41, and warns about possible video issues if constantly at -60.
Is RSSI -72 good?
A received signal strength indication WiFi value of -72 is acceptable but not amazing. Using the methods described in this article, you should be able to improve it until you reach at least -60 (remember, the closer you get to zero, the better).
What is the Significance of the RSSI Number
“The RSSI number represents the amount of power that is lost during the transmission of a signal. In practical scenarios, there is always some degree of power loss, hence achieving an RSSI value of -20 is usually considered optimal.
Is RSSI Expressed in dB or dBm Units?
Although RSSI does not have any official units, it is occasionally used interchangeably with dBm, which measures power level in decibels (dB) relative to one milliwatt (mW).